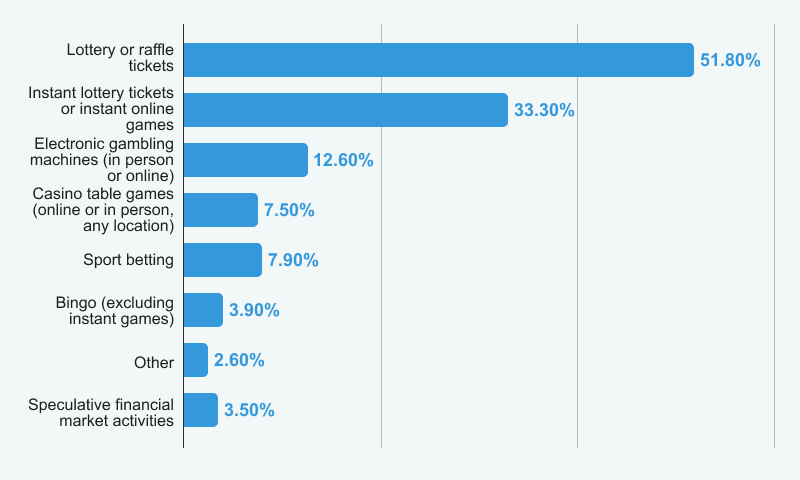
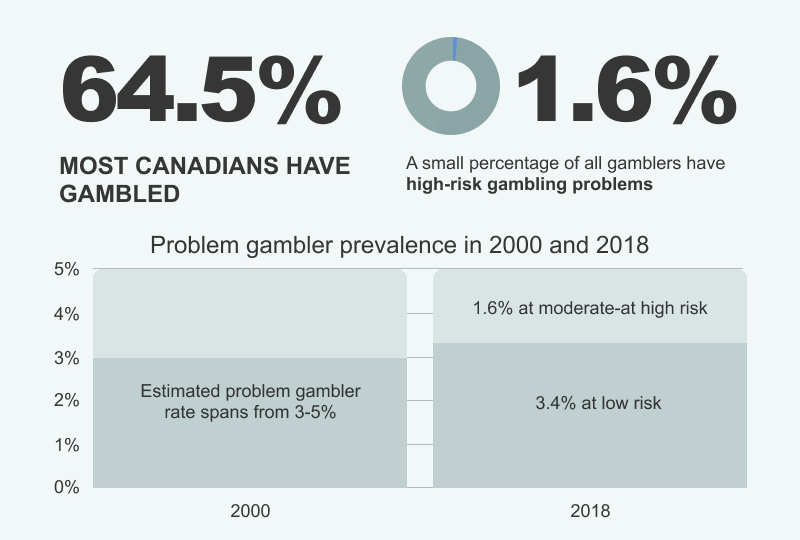
A study from the year 2000, during the early days of online gambling, indicated that there was significant discourse surrounding online gambling at that time, with concerns that it could foster addiction. This stems from the ease of accessing casino games from home, especially affecting younger players who are adept with internet technology. At that time, the prevalence of gambling-related issues among Canadians was estimated to be around 3-5%.
A more recent report dating back to 2018 indicated that 3.4% of Canadians (about 636,000 individuals) were identified as being at a low risk for gambling-related harms. In contrast, 1.6% (about 304,000 individuals) experienced moderate to severe gambling risks. Notably, 64.5% of Canadians reported having gambled at least once over the past year. This implies that only a minor fraction of Canadians confront severe gambling problems.
By comparing data from the 2000 study with more recent findings, we sought to ascertain whether the convenience and accessibility of online gambling have influenced the rates of gambling-related harms. Our analysis showed that the problematic gambling prevalence from 2000 to 2018 remained unchanged , staying consistent at around 5%.
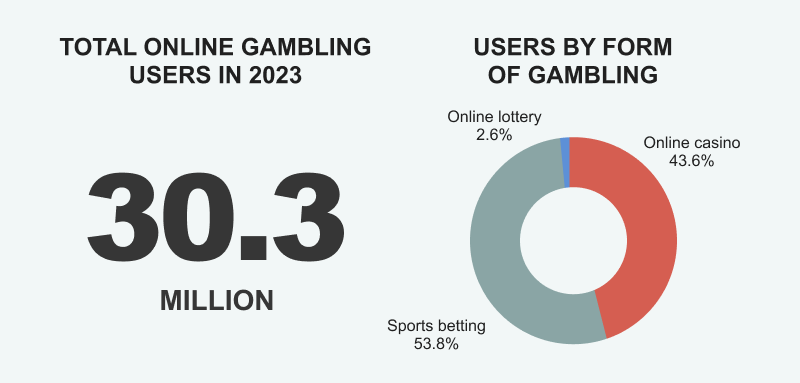
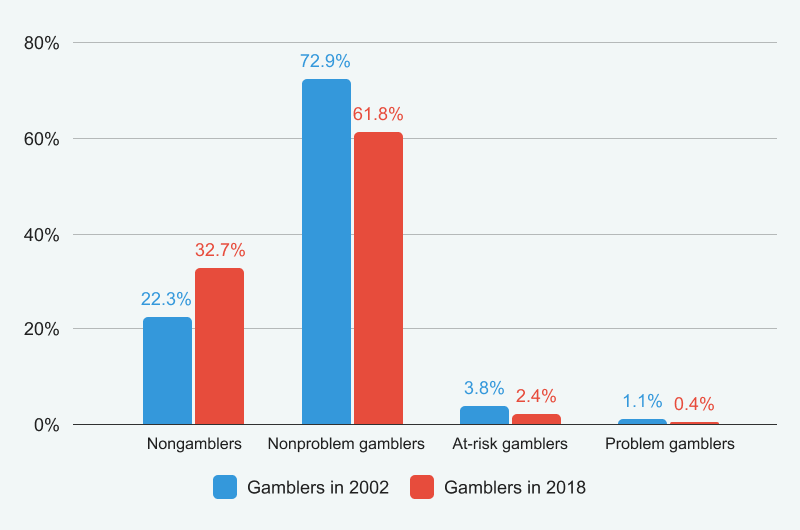
Problem gamblers in Canada (information sourced from Statistics Canada)
A further study released in 2021 in the Canadian Journal of Psychiatry corroborates our earlier observations, indicating a reduction in the number of problem gamblers and suggesting improvements in the overall scenario.
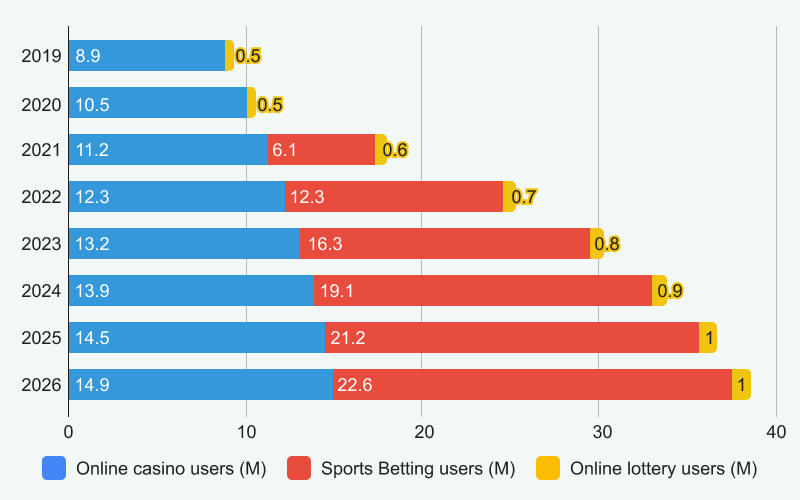
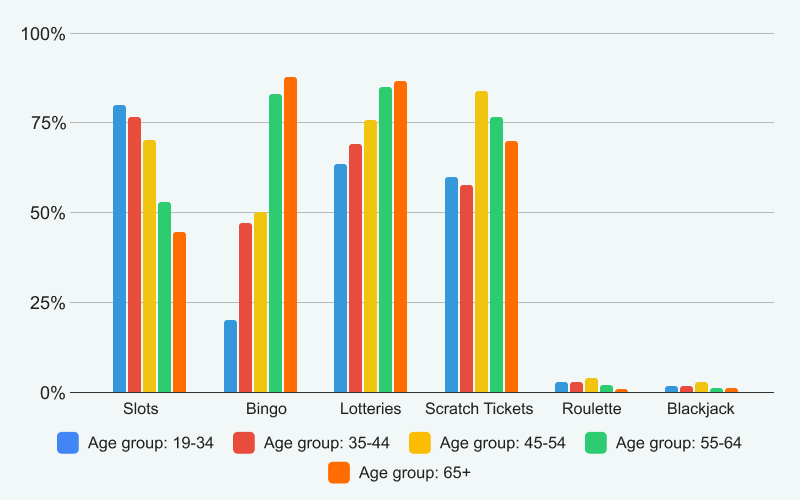
Trends in gambling behavior over the years (data from National Library of Medicine)
The data reveals that between 2002 and 2018, there was a 10.4% reduction in the number of individuals who gamble . While the rate of non-problem gamblers also decreased, this aligns with the overall downturn in gambling participation in the nation.
The critical statistics to focus on are the percentages of at-risk gamblers and problem gamblers – both have seen declines of 1.4% and 0.7%, respectively. The most recent data suggests that issues related to gambling in Canada have become somewhat less common. Nonetheless, further research will be necessary to gain a clearer understanding of the current landscape, as the latest study analyzing this issue was completed six years ago.
Individuals from Low-Income Backgrounds Are More Susceptible to Gambling Issues
The occurrence of gambling addiction is closely tied to socioeconomic factors . A smaller fraction of Canadians with lower economic status engage in gambling when compared to their higher-income counterparts. Nevertheless, individuals from low-income backgrounds are at a heightened risk of developing compulsive gambling behaviors.
According to a 2018 Canadian Community Health Survey, those from lower-income households are less inclined to gamble than those from wealthier households, yet they experience a greater likelihood of gambling-related challenges.
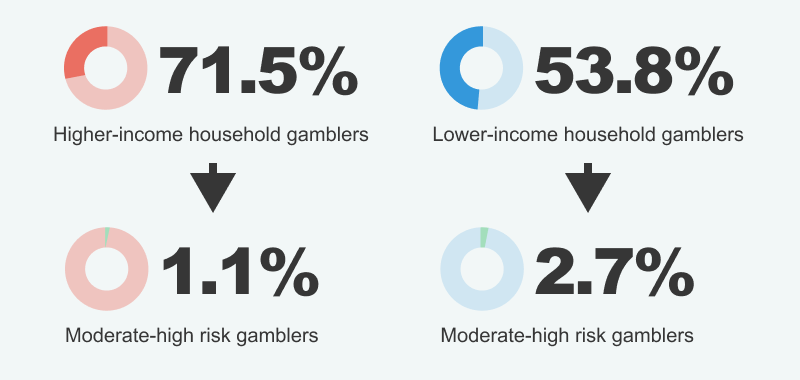
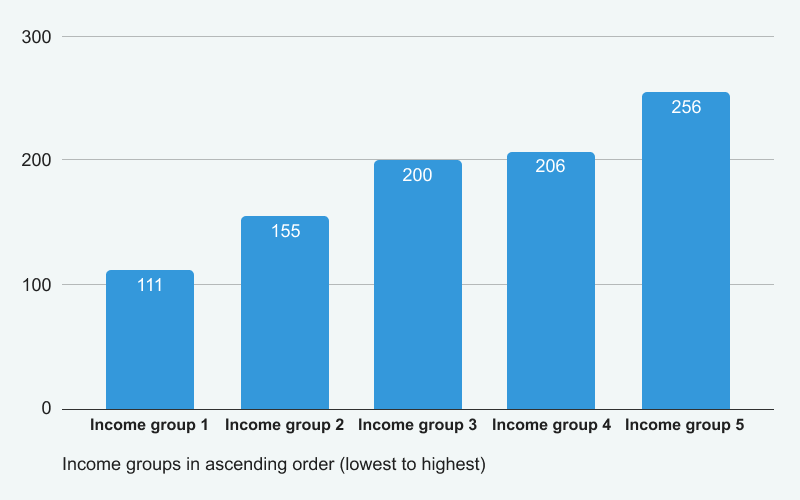
High-income versus low-income gamblers (data from Statistics Canada)
In 2018, a reported 71.5% of Canadians from affluent households participated in gambling, with only 1.1% classified as being at moderate to severe risk for problem gambling. In stark contrast, among lower-income households, 2.7% of the 53.8% who gambled faced moderate to severe gambling risks. This statistic signifies that individuals from low-income backgrounds are nearly twice as prone to becoming addicted to gambling.
The association between gambling issues and lower income levels may arise from a perception of gambling as a means to enhance financial stability. Additionally, those with higher incomes are generally more capable of managing potential losses from gambling, making them less impacted overall. It is clear that compulsive gambling stems from various factors, indicating that other elements play a significant role.
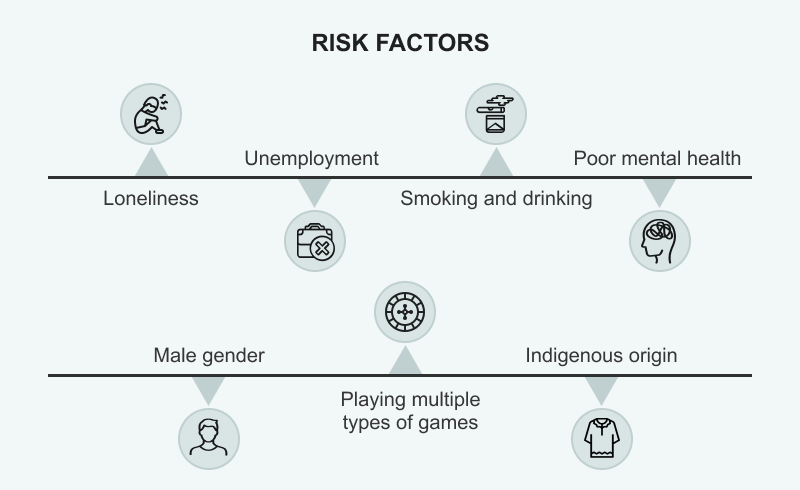
Identifying risk factors related to gambling issues in Canada (data from Statistics Canada)
Several other elements correlate with gambling issues, including:
- Being single or divorced often results in a lack of social support, making one more susceptible to excessive gambling behaviors;
- Unemployment can result in gambling being seen as an effective coping mechanism;
- Daily smoking and heavy drinking are recognized as having common addiction triggers that intersect with gambling, impacting the brain's neurobiology;
- Poor mental health can diminish the barriers that prevent compulsive gambling;
- The prevalence of gambling-related challenges is notably higher among males compared to females;
- Individuals who participate in multiple gambling forms are more likely to develop compulsive gambling behaviors;
- Indigenous communities are three times more likely to experience moderate to severe gambling risks, which can be linked to socioeconomic factors.
Our conclusion suggests that the convergence of specific risk factors may contribute to gambling problems among vulnerable groups. Fortunately, Canadians experience a relatively stable social and economic environment, leading to a smaller number of problem gamblers. However, emerging trends and changes in the gambling sector could introduce new challenges that influence the escalation of gambling-related harms.
Does Advertising Contribute to Gambling Issues?
The expansion of the online gaming sector has resulted in a notable increase in gambling advertisements , especially online. These promotions have not only proliferated but also frequently feature endorsements from influencers and celebrities. Gambling companies are keen to leverage these marketing channels, prompting concerns within the Canadian populace.
The situation intensified with the launch of the Ontario iGaming market in April 2022, which spurred a rapid influx of new Ontario online casinos , leading to a significant rise in advertising volume. In response, Ontario has implemented measures such as restricting the use of celebrities, athletes, and influencers in gambling promotions starting February 2024.
An Ipsos survey conducted in 2022 revealed that around half of Canada's population perceives the amount of gambling advertising as excessive . The majority of Canadians concur that measures should be taken to limit such advertisements.
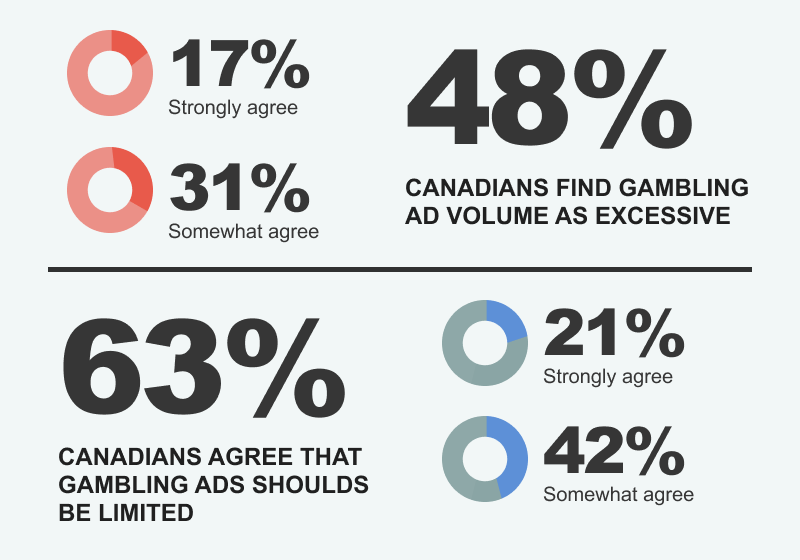
Survey findings on gambling advertising (data from Ipsos)
Based on the survey responses, it appears that most Canadians maintain a moderate stance concerning gambling advertising , as only roughly 20% of respondents strongly affirmed the excessive nature of these ads and the need for curbs on their frequency.
The primary concern surrounding gambling advertising is its potential to attract children and young adults to gambling activities at an early age. A review by The Campaign to Ban Ads for Gambling has highlighted a connection between exposure to gambling ads and a more favorable perception of gambling, leading to increased gambling engagement. Moreover, evidence suggests that the youth demographic and those who are already vulnerable to gambling addiction are particularly susceptible to influence.